Common Foot Problems: Top 10 Issues and How to Treat Them Effectively
The human foot is a complex structure that bears the weight of the body and enables movement. Due to daily wear and tear, a variety of conditions can affect the feet — from infections and inflammation to deformities and nerve damage. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of these conditions is essential for proper foot care.
Here’s an overview of ten prevalent foot problems, their causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
Athlete’s Foot – A Common Foot Problem Caused by Fungal Infection
Athlete’s foot is a common fungal skin infection that typically develops between the toes but can spread to other areas of the foot.
Causes:
- Exposure to damp, communal areas like gym showers, locker rooms, or public pools.
- Wearing tight or non-breathable footwear that traps moisture.
- Sharing towels or shoes with others.
Symptoms:
- Persistent itching, especially between the toes.
- Cracked or peeling skin.
- Formation of small blisters.
- Redness and scaling.
Treatment:
- Over-the-counter antifungal sprays, creams, or powders.
- Keeping feet clean and thoroughly dry, especially between the toes.
- Using a separate towel for infected feet.
- Severe or spreading infections may require prescription oral antifungal medication.
Bunions – A Painful Foot Condition Among Common Foot Problems
A bunion is a bony protrusion that forms on the side of the foot near the base of the big toe, often causing the toe to angle inward.
Causes:
- Wearing narrow, tight, or high-heeled shoes.
- Genetic predisposition (family history).
- Underlying health conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Symptoms:
- Noticeable bump on the side of the foot.
- Pain or soreness near the big toe joint.
- Corns or calluses where toes overlap.
- Restricted toe movement.
Treatment:
- Switching to wider, more comfortable shoes.
- Using bunion pads or orthotic inserts.
- Physical therapy and toe splints.
- Surgical correction for severe cases.
3. Diabetic Neuropathy – Nerve-Related Foot Issue in Diabetics
Diabetic neuropathy involves nerve damage, often affecting the feet, and is a common complication of diabetes.
Causes:
- Long-term elevated blood sugar levels.
- Additional risk factors include obesity, high blood pressure, smoking, and high cholesterol.
Symptoms:
- Tingling or burning sensations.
- Loss of feeling or numbness in the feet.
- Pain or discomfort, particularly at night.
- Increased risk of unnoticed injuries or infections.
Treatment:
- Strict blood sugar management.
- Regular foot inspections and podiatric care.
- Pain management through medications.
- Wearing protective footwear to prevent injuries.
4. Ingrown Toenails One of the Most Common Foot Problems Causing Pain
An ingrown toenail develops when the edge of a toenail grows into the surrounding skin, leading to inflammation and sometimes infection.
Causes:
- Improper nail trimming (cutting nails too short or at an angle).
- Wearing tight shoes that put pressure on the toes.
- Toe injuries or frequent running.
Symptoms:
- Swelling and redness around the nail.
- Pain and tenderness, especially when pressure is applied.
- Pus discharge in case of infection.
Treatment:
- Soaking feet in warm water and keeping them clean.
- Wearing open-toed or comfortable shoes.
- Pain relievers to ease discomfort.
- Infected or persistent cases may require minor surgery and antibiotics.
5. Plantar Fasciitis A Common Cause of Heel Pain and Foot Discomfort
Plantar fasciitis is a condition where the thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot becomes inflamed, leading to heel pain.
Causes:
- Overuse from running or standing for long periods.
- Flat feet or high arches.
- Sudden increase in physical activity.
- Obesity or tight calf muscles.
Symptoms:
- Sharp pain in the heel, especially in the morning or after rest.
- Discomfort that worsens with activity.
- Pain when climbing stairs or standing for extended periods.
Treatment:
- Rest, ice application, and anti-inflammatory medication.
- Daily stretching exercises for the foot and calf.
- Supportive footwear or custom orthotics.
- Physical therapy or corticosteroid injections in severe cases.
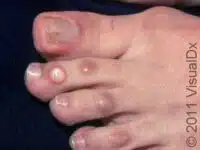
6. Blisters A Frequently Overlooked Foot Problem
Blisters are fluid-filled sacs that form on the skin due to friction or irritation, commonly affecting the feet during prolonged activity.
ALSO VISIT
Causes:
- Wearing poorly fitting or stiff shoes.
- Excessive moisture from sweat.
- Extended walking, hiking, or running.
Symptoms:
- Raised, fluid-filled bump on the skin.
- Pain, tenderness, or burning sensation.
- Possible redness around the affected area.
Treatment:
- Avoid popping the blister; allow it to heal naturally.
- Use padded bandages or blister plasters.
- Keep the area clean and dry.
- Seek medical attention if signs of infection develop (pus, redness, heat).
7. Corns Thickened Skin as a Result of Common Foot Issues
Corns are thickened areas of skin that develop in response to pressure or friction, most often on the toes or soles.
Causes:
- Wearing tight or high-heeled shoes.
- Walking barefoot or in shoes without socks.
- Abnormal toe structure or gait.
Symptoms:
- Small, hard bump surrounded by inflamed skin.
- Pain or discomfort when walking or wearing shoes.
- Yellowish, hardened skin layers.
Treatment:
- Soaking feet in warm water and gently filing the corn with a pumice stone.
- Regularly moisturizing the area.
- Wearing properly fitted shoes.
- In persistent cases, a podiatrist may remove the corn or recommend padding and orthotics.
8. Heel Spurs A Bone-Related Foot Condition Often Misdiagnosed
A heel spur is a calcium deposit causing a bony protrusion on the underside of the heel bone, often linked to plantar fasciitis.
Causes:
- Chronic strain on foot muscles and ligaments.
- Long periods of standing or walking on hard surfaces.
- Inflammatory diseases like arthritis.
- Excess body weight.
Symptoms:
- May cause no symptoms in some individuals.
- Heel pain during walking or standing.
- Inflammation and swelling at the front of the heel.
Treatment:
- Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Stretching exercises and physical therapy.
- Use of orthotics for added support.
- Surgical removal is rare but may be necessary for ongoing pain.
9. Claw Toe A Foot Deformity Among Common Foot Conditions
Claw toe is a deformity where the toe bends upward at the joint closest to the foot and downward at the middle joint, resembling a claw.
Causes:
- Nerve damage from conditions like diabetes or alcoholism.
- Injuries or imbalances in foot muscle strength.
- Wearing tight shoes for extended periods.
Symptoms:
- Toes bent into an abnormal claw-like shape.
- Difficulty wearing shoes or walking comfortably.
- Corns or calluses may form due to friction.
Treatment:
- Switching to shoes with a wide toe box.
- Toe stretches and strengthening exercises.
- Orthotic supports.
- In advanced cases, surgical intervention may be needed.
10. Metatarsalgia Forefoot Pain Caused by Common Foot Strain Issues
Metatarsalgia is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot.
Causes:
- High-impact sports like running.
- Wearing high heels or shoes with thin soles.
- Bunions or toe deformities.
- Excessive pressure from obesity or foot structure.
Symptoms:
- Burning or aching pain in the ball of the foot.
- Sensation of having a pebble under the foot.
- Pain that increases with standing or activity.
Treatment:
- Rest and applying ice.
- Wearing cushioned shoes or using metatarsal pads.
- Choosing low-impact activities like swimming or cycling.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the feet.
Summary
Foot problems are common and can range from mild irritations like blisters and corns to more serious conditions such as diabetic neuropathy and deformities like bunions or claw toe. Prompt attention and proper care are essential to prevent complications.
If symptoms persist, worsen, or lead to difficulty in walking, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider or podiatrist for a thorough diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early intervention can improve comfort, mobility, and overall foot health.